The Role of Magnesium in our Body and How it Helps Treat Depression

Table Of Contents
The Benefits in Taking Magnesium
Magnesium is a mineral that is found in many foods that plays an important role in the body.
Magnesium:
- Helps regulate nerve and muscle function
- Keeps heart rhythm steady
- Supports a healthy immune system
- Keeps bones strong
- Helps regulate blood sugar levels
- Promotes normal blood pressure
- Is involved in energy metabolism
What is Depression
Depression is a mental illness that affects 350 million people globally and is predicted to be the leading cause of disease by 2030. Antidepressant trials of sufficient dose and duration result in 50% of patients achieving relief. Even after the additional treatments, 20% still suffer from symptoms after 2 years.
Some research has shown that magnesium may help with depression symptoms in people who are deficient in this mineral.
The study on magnesium supplementation on mild to moderate depression
This study was designed to see if magnesium supplementation would help people with mild-to-moderate depression.
The study on magnesium was done in an academic medical center. 112 randomized participants were to take magnesium immediately or at the 7th week.
Participants were given four 500 mg tablets of MgCl2 (a dietary supplement) daily for a total of 248 mg of elemental magnesium per day.
They were followed every 2 weeks via telephone. Their PHQ-9 score, Generalized Anxiety Disorders-7, Modified Morisky Scale, PhenX Tobacco Smoking Status Questionnaire for Adults, and PhenX Alcohol 30 Day Quantity and Frequency Questionnaire were collected.

The results of the study
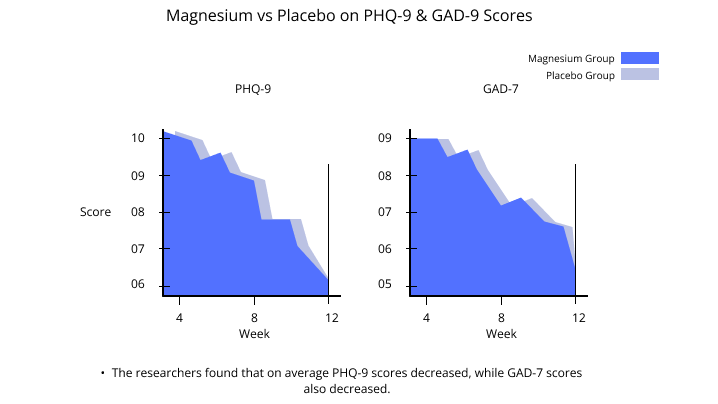
The study found that magnesium supplementation reduced the severity of depression and anxiety. The supplement was most effective for those with moderate depression and anxiety, but still helped those with more severe cases. The study also found that magnesium reduced headaches and did not have any other side effects.
The researchers found that on average PHQ-9 scores decreased, while GAD-7 scores also decreased.
Analysis on subgroups indicated that magnesium was effective regardless of age or gender.
What are PHQ-9 and GAD-7 Tests
The Patient Health Questionnaire-9 (PHQ-9) is a brief, 9-item questionnaire that measures the severity of depression symptoms over the past 2 weeks. The PHQ-9 is designed to be used by patients or clinicians to quickly assess the severity of depression and monitor changes in symptoms over time.
The GAD-7 is a 7-item scale that measures the severity of anxiety symptoms in the past week. The items are scored on a scale from 0 to 3, with higher scores indicating more severe symptoms.
The Conclusion
Daily supplementation of 500 mg tablets of magnesium chloride per day might significantly decrease depression and anxiety symptoms regardless of age, gender, and baseline severity of depression.
While the cross-over design of this trial is robust in controlling internal biases, it would be reassuring to see the results replicated in larger clinical trials that test long-term efficacy and provide additional data on subgroups.
However, this trial showed that magnesium supplements might be a fast, safe, and easily accessible alternative to starting or increasing the dose of antidepressant medications.
Reference
Role of magnesium supplementation in the treatment of depression: A randomized clinical trial
Related Posts



Quick Links
Legal Stuff