Magnesium Sulfate's Analgesic Effect During Total Intravenous Anesthesia
Table Of Contents
The Use and Side Effects of Opioids
Opioids, like remifentanil, are usually used during surgery as pain relievers, but they have many adverse effects like nausea, vomiting, and breathing problems.
The objective of this study was to see if magnesium sulfate would work better than opioids for pain relief during surgery. It also looked at how much of an anesthetic and sedative drug, known as propofol, patients needed, how well they felt after surgery, and how stable their blood pressure was during surgery.
The Study on Magnesium Sulfate for Pain Relief
43 patients participated in this study. All were scheduled to have weight-loss surgery and were placed under general anesthesia. They were randomly put into two groups: 23 got remifentanil, and 20 had magnesium sulfate as intravenous analgesics (drugs for pain relief) during operation.
Fentanyl was the rescue analgesic in case more was needed. Researchers monitored the blood pressure continuously throughout the procedure. The pain intensity was recorded upon awakening, six hours after, and on the first three hours of the following day.
The Results
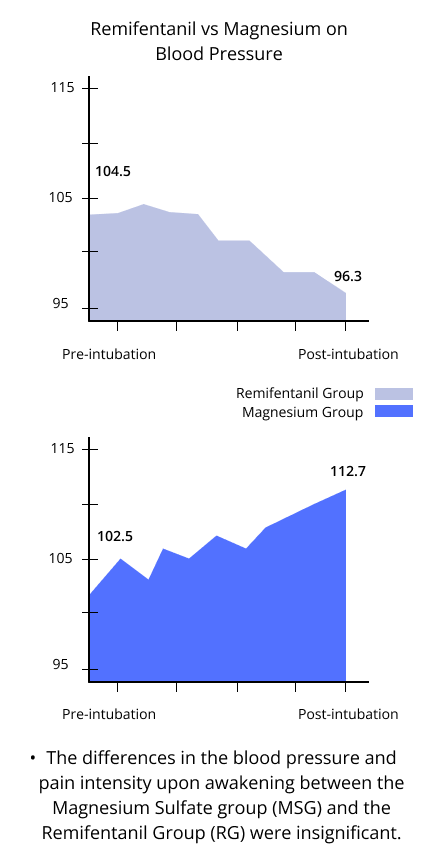
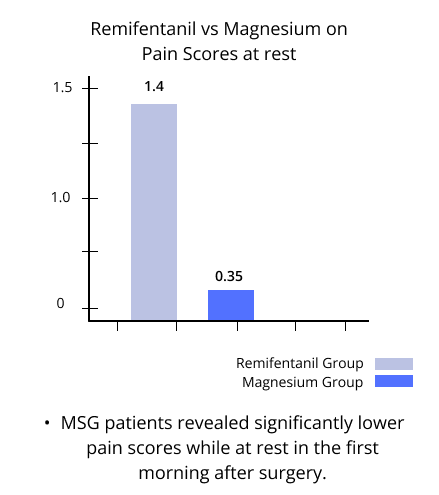
The differences in the blood pressure and pain intensity upon awakening between the Magnesium Sulfate group (MSG) and the Remifentanil Group (RG) were insignificant. However, MSG patients revealed significantly lower pain scores while at rest in the first morning after surgery.
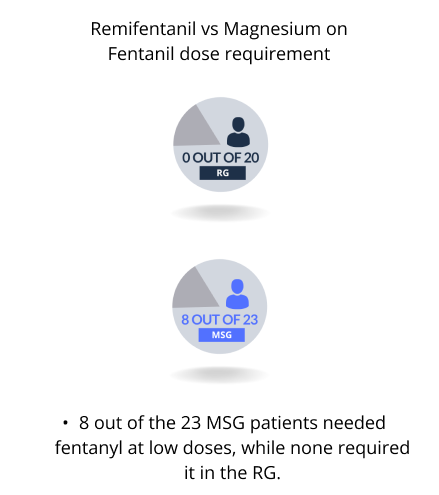
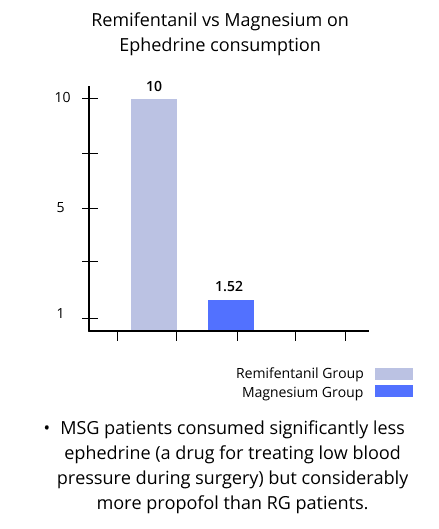
8 out of the 23 MSG patients needed fentanyl at low doses, while none required it in the RG. MSG patients consumed significantly less ephedrine (a drug for treating low blood pressure during surgery) but considerably more propofol than RG patients.
The stable blood flow and comparable health condition of patients in the groups receiving remifentanil or magnesium sulfate as an analgesic during surgery may lead to reduced use of opioids and their resulting side effects.
The Conclusion
Magnesium sulfate can be considered a safe and effective option for controlling pain during surgery when avoiding or decreasing opioid use is required.
Reference
Analgesic Effect of Magnesium Sulfate During Total Intravenous Anesthesia
Related Posts


Quick Links
Legal Stuff