Can Intravenous Magnesium Sulfate be an Effective Hypotensive Anesthesia Clinical Test

Table Of Contents
Why is General Anesthesia Preferable During Surgery?
Sinus surgery is used to treat people with sinus problems. During surgery, if there is a lot of bleeding, visibility in the area being operated on becomes a problem. Most people choose general anesthesia because it makes you feel better than topical (applied on the skin) anesthesia, and it uses hypotensive anesthesia. This technique involves intentionally lowering blood pressure to minimize blood loss during surgery.
Is Magnesium an Effective Blood Pressure-Lowering Agent?
Intravenous magnesium sulfate may be an effective agent for lowering blood pressure because its effect on cell proteins makes them more stable, which can help keep blood pressure down. Magnesium sulfate also acts as a vasodilator making veins wider so blood can flow more easily.
This study aimed to evaluate the effects of intravenous magnesium sulfate technique of hypotensive anesthesia.
The Study on Magnesium Sulfate in Lowering Blood Pressure During Surgery
60 patients undergoing endoscopic sinus surgery were assigned randomly into one of the two groups. The magnesium group received magnesium sulfate, and the control group received sodium chloride. These were administered before injecting the anesthesia.
The Results
The following are the findings in the magnesium group:
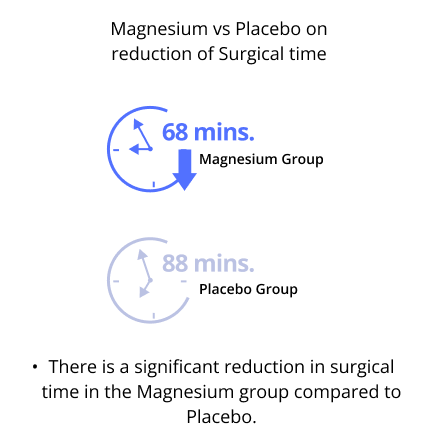
- Significant reduction in surgical time
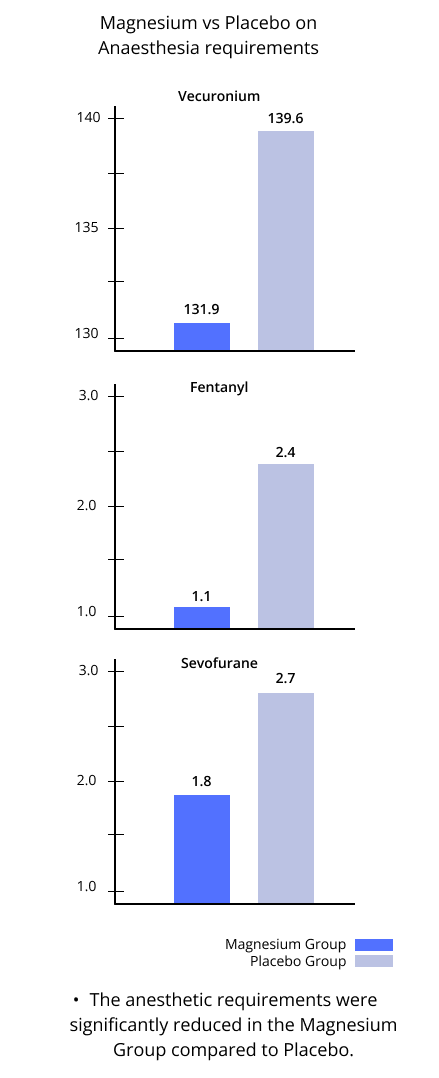
- The anesthetic requirements were significantly reduced - Blood loss was reduced
- The operative field conditions and heart rates were considerably better at 5, 15, 30, 45, and 60 min and the end of surgery. - And the anesthetic time was 10 min longer in the magnesium group, thus presuming a prolongation in anesthetic emergence
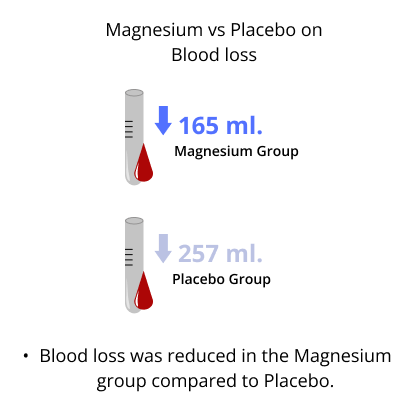
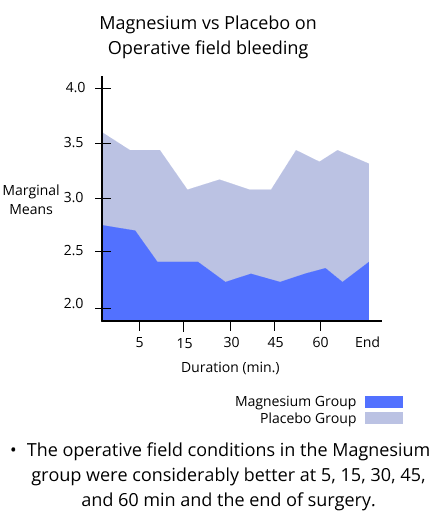
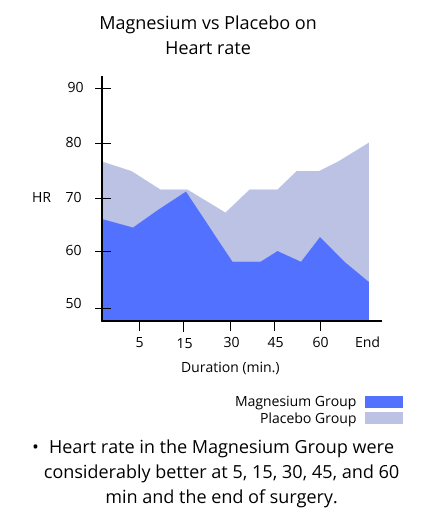

There were no episodes of hypotension (low blood pressure), arrhythmia (irregular heartbeat), or reflex tachycardia (fast heart rate) during magnesium sulfate infusion, and no patient had rebound hypertension upon discontinuing magnesium sulfate infusion.
The Conclusion
Magnesium sulfate led to a reduction in blood pressure, heart rate, blood loss, anesthetic dose requirements, and duration of surgery.
Reference
Related Posts


Quick Links
Legal Stuff